let’s take a quick look at some injection molding processes used in fabricating medical devices.
Plastic(Regular) Injection Molding
Injection molding involves liquifying plastic polymers under high temperatures before reshaping or molding them into the desired shape in an aluminum or steel die mold. Plastic injection molding is highly valuable to the medical industry, as the process occurs under hygienic conditions. The high temperatures for melting the plastics ensure they are free of contaminants and microbes that may harm patients’ health.
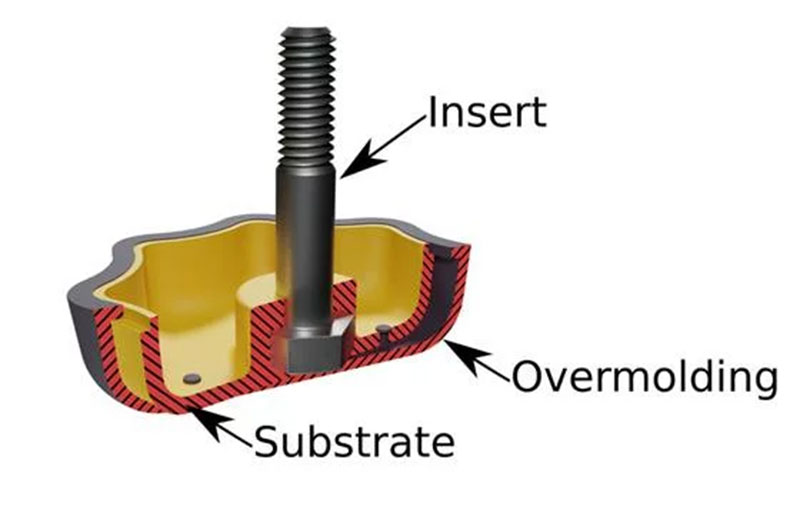
Overmolding
Overmolding is a type of injection molding that involves molding one or two components over an already molded and cured structure – the substrate. The process is called two-shot molding because it requires at least two steps, giving it a long production cycle. However, this technique is valuable to plastic manufacturing, especially in fabricating handles and components that require a firm grip.
Insert Molding
Insert molding is similar to overmolding in that a secondary component is molded over an already molded part – the insert. Unlike overmolding, insert molding is a single process, as the substrate (inserts) is a pre-existing structure. Also, this technique is not limited to plastic parts, as the inserts molded over can be made of metals or alloys.
Liquid Silicone Injection Molding
This process involves heating silicone to a molten state and then remolding it into the desired shapes of the medical product. Silicone is a typical plastic polymer suitable for use in the medical industry.
However, due to silicone molds are not as durable as aluminum or steel molds, silicone injection molding is usually only suitable for producing small quantities of medical parts, especially in the initial stages of medical prototyping and product development.


